Advanced NMEA Data Logger - Online help | Advanced NMEA Data Logger
About Advanced NMEA Data Logger
Advanced NMEA Data Logger inputs NEAM data stream from GPS, navigation or any other NMEA compatible device directly into file, Excel, Access, database or any Windows application. Advanced NMEA Data Logger provides real-time data collection from any device or instrument.
Advanced NMEA Data Logger captures serial or network data, custom parses it to your needs, then extract bits of data from data packets and transfers the data to any Windows or DOS application - either by sending keystrokes to the application's window, by passing the data through DDE (Dynamic Data Exchange) conversations, ODBC, OLE.
Key features of Advanced NMEA Data Logger are:
•capability to log multiple ports at the same time. Each port may have fully different settings.
•supports all talker types (GPS, Heading, Velocity sensors etc).
•captures all standard NMEA sentences and some proprietary sentences for Garmin, SiRFand StarLink devices.
•supports custom baud rates.
•supports date/time stamping;
•supports aggregation of multiple sentences to one data record.
•outputs received data without any changes to a log file.
•advanced data parsers that allows you to parse, filter and format your source data.
•data export to ready-to-use MS Excel files.
•data export to any ODBC-compatible database (MS SQL, Oracle, MS Access, dBase and others).
•Advanced NMEA Data Logger can run as DDE or OPC server and can export all received data.
•Advanced NMEA Data Logger can use direct connection (use OLE) to Microsoft Excel and write data directly to rows or columns.
•program messages logging.
•simple, menu-driven step by step set-up - programming is not required to configure the software to collect data.
•many plugin modules that extending program features.
•It supports various operating systems. The logger runs on all versions starting from Windows 2000, including 32 and 64-bit systems.
Advanced NMEA Data Logger also transmits requests or commands over a network connection or serial port to control or query your instruments directly from Advanced NMEA Data Logger over ASCII protocol.
Unlike most other serial logging applications, Advanced NMEA Data Logger can run as a service so that it starts as soon as the operating system starts and doesn't require a user to log in and run it. It will continue to run even as a user logon and logoff the workstation.
It is extremely easy to use! The configuration process is fully menu-driven and has complete, context-sensitive, online help. You can easily customize all input to your exact specifications. Once you see how easy it is to use Advanced NMEA Data Logger, you will never again take data readings by hand!
Typical usage
A typical application for Advanced NMEA Data Logger is to log and aggregate data from one or more NMEA devices to disk or a software replacement for a hardware data logger.
Applications examples
•Data logging systems;
•Remote control systems;
•Remote control of displays and signaling.
Company home page: https://www.aggsoft.com/
Software home page: https://www.aggsoft.com/nmea-data-logger.htm
Glossary
ASCII - An acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. ASCII files are plain, unformatted text files that are understood by virtually any computer. Windows Notepad and virtually any word processor can read and create ASCII files. ASCII files usually have the ".TXT" extension (e.g., README.TXT).
Binary File - A file that contains data or program instructions written in ASCII and extended ASCII characters.
Bit - A binary digit in the binary numbering system. Its value can be 0 or 1. In an 8-bit character scheme, it takes 8 bits to make a byte (character) of data.
Bytes - A collection of eight bits that represent a character, letter or punctuation mark.
Cable - Transmission medium of copper wire or optical fiber wrapped in a protective cover.
Client/Server - A networking system in which one or more file servers (Server) provide services; such as network management, application, and centralized data storage for workstations (Clients).
COM port - Short for a serial communication port. Most serial communication software communicates with a computer through a communication port, and most IBM and IBM-compatible computers support up to four serial ports COM1, COM2, COM3, and COM4. Additional ports can be added by adding additional hardware.
Data bits - A group of bits (1's and 0's) that represents a single character or a byte. Typically, there are seven or eight data bits. During an asynchronous communication (e.g., BitCom connecting to CompuServe), each side must agree on the number of data bits. Data bits are preceded by a start bit and followed by an optional parity bit and one or more stop bits.
DNS (Domain Name System) - A DNS server lets you locate computers on a network or the Internet (TCP/IP network) by the domain name. The DNS server maintains a database of domain names (hostnames) and their corresponding IP addresses. The IP address "8.8.8.8", corresponds to the DNS name www.google.com.
Flow control - A method of controlling the amount of data that two devices exchange. In data communications, flow control prevents one modem from "flooding" the other with data. If data comes in faster than it can be processed, the receiving side stores the data in a buffer. When the buffer is nearly full, the receiving side signals the sending side to stop until the buffer has space again. Between hardware (such as your modem and your computer), hardware flow control is used; between modems, software flow control is used.
Handshaking - is how the data flow between computers/hardware is regulated and controlled. Two distinct kinds of handshaking are described: Software Handshaking and Hardware Handshaking. An important distinction between the kinds of signals of the interface is between data signals and control signals. Data signals are simply the pins which actually transmit and receive the characters, while control signals are everything else.
Internet - A global network of networks used to exchange information using the TCP/IP protocol. It allows for electronic mail and the accessing ad retrieval of information from remote sources.
IP, Internet Protocol - The Internet Protocol, usually referred to as the TCP/IP protocol stack, allows computers residing on different networks to connect across gateways on wide-area networks. Each node on an IP network is assigned an IP address, typically expressed as 'xx.xx.xx.xx'.
IP address (Internet Protocol address) - The address of a computer attached to a TCP/IP network. Every client and server station must have a unique IP address. Client workstations have either a permanent address or one that is dynamically assigned to them each dial-up session. IP addresses are written as four sets of numbers separated by periods; for example, 198.63.211.24.
LAN (Local Area Network) - A network, connecting computers in a relatively small area such as a building.
NIC, Network Interface Card - A card containing the circuitry necessary to connect a computer to a particular network media. Typically, the NIC plugs into the computer's accessory bus, (PCI, USB, etc.) and provides a network connection such as 10baseFL (fiber Ethernet), thin-net, AUI, etc.
PC - abbreviation for a Personal Computer.
Parity - In data communications, parity is a simple procedure of checking the integrity of transmitted data. The most common type of parity is Even, in which the number of 1's in a byte of data adds up to an even number, and None, in which a parity bit is not added.
Ports - is a connection point for a cable.
Protocol - is a formal description of a set of rules and conventions that govern how devices on a network exchange information.
RS232, RS423, RS422, AND RS485 - The Electronics Industry Association (EIA) has produced standards for RS232, RS423, RS422, and RS485 that deal with data communications. EIA standards where previously marked with the prefix "RS" to indicate the recommended standard. Presently, the standards are now generally indicated as "EIA" standards to identify the standards organization.
Electronic data communications will generally fall into two broad categories: single-ended and differential. RS232 (single-ended) was introduced in 1962. RS232 has remained widely used, especially with CNC control builders. The specification allows for data transmission from one transmitter to one receiver at relatively slow data rates (up to 20K bits/second) and short distances (up to 50' @ the maximum data rate). This 50' limitation can usually be exceeded to distances of 200' or more by using low capacitance cable and keeping the data rates down to 9600 baud and lower.
RTS/CTS Hardware handshaking - uses additional wires to tell a sending device when to stop or start sending data. DTR and RTS refer to these Hardware handshaking lines. You can select whether you need to use DTR or RTS individually or use both lines for hardware handshaking. See also Xon/Xoff.
TCP/IP, Transport Control Protocol / Internet Protocol - TCP and IP are communications protocols, that is, structured languages in which data is communicated between one process and another, and between one network and another. TCP/IP is implemented in a multi-level layered structure.
TCP/IP is the 'glue' that ties together the many heterogeneous networks that make up the Internet.
Stop bits - In data communication, one or two bits used to mark the end of a byte (or character). At least one stop bit is always sent.
System requirements
Windows 2000 Professional - Windows 10 (2019), including x64 and x86 OS, Workstation, and Server OS.
It is necessary to have at least one free COM port, not busy by any device (mouse, for example) to connect an external device.
It is necessary to have at least one working network interface (card) in your PC.
Installation process
If any beta-version was installed on your computer, remove it.
Quit of the working Advanced NMEA Data Logger on installation time.
Run an installation file.
By default, the installation wizard installs Advanced NMEA Data Logger in the "C:\Programs Files\Advanced NMEA Data Logger" or "C:\Programs Files (x86)\Advanced NMEA Data Logger" directory of your system disk, but you can change this path.
In the standard distributive of Advanced NMEA Data Logger are no additional modules files, which you can download from our site.
Getting started
After you have successfully installed Advanced NMEA Data Logger, use the following simple steps to configure and run it.
Open the Advanced NMEA Data Logger program from the Start Menu.
At program run, you get into the main program window (fig. 1), main elements of which are the main menu, the data window, the program messages list, and the status bar.
-The data window shows incoming data before or after processing. You can configure the data view mode in the settings
-The drop-down box at the bottom shows all logged program info, warning, and error messages.
-The status bar shows the current state of the selected data source, errors on the data interface, and how many bytes were sent or received.
-The toolbar above the data window provides fast access to the configuration.
-The main menu above the toolbar allows you to edit the program settings ("Options - Program settings..."), manage configurations, open the current logfile from the "File" menu (fig. 2).
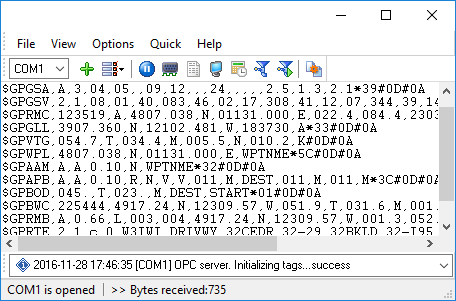
Fig. 1. Main program window

Fig. 2. "File" menu item
By default (after installation), the program has not any data sources configured. If the list of data sources on the toolbar is empty, then the program will ask you to add a new configuration. Otherwise, the program will fill in the list of data sources and try to start logging of data sources configured. Yes, of course, all your settings are being saved while exiting from the program and loaded during the program start.
Set-Up is as Easy as 1-2-3
Step 1. Configure one or more data sources.
Click the "Add configuration" button on the toolbar with a big green plus and choose communication parameters for your device. The "COM Port settings" tab of the "Configuration options" dialog lets you configure your settings.
Step 2. Configure log file.
Select the "Log file" header in the configuration dialog window and enable logging for a necessary data direction.
Step 3. Define how you want the NMEA data to be parsed and translated.
The "Plugin" button on the toolbar in the main window or "Modules" tab in the dialog window lets you specify how to parse, filter and format your data to the fit the exact format required by your application. It also lets you pre-define automatic output strings to be sent to an external device.
Now, the program process and exports data from one or multiple data sources.
Introduction
The program can work with any serial devices. Before configuring our software, the following conditions should be executed:
•The device should have an RS-232 serial port interface (you need any additional hardware converter for the RS-485 interface).
•The device is configured to send data to a serial port with or without requests from a computer side.
•You know all information about serial port parameters of your device (If your device uses hardware or software flow control (please, read your device's datasheet), then you should know about flow control type).
•Device's serial port is connected with a computer serial port using a cable (a null-modem or other special cable).
•Computer's COM port, to which your device is connected is not busy, for example by another program.
How to configure port parameters, you can read in the next "Serial port settings" chapter.
The program can work with any network interface cards (NIC). Before configuring our software, the following conditions should be executed:
•If your computer has more than one network interface card (NIC) then Advanced NMEA Data Logger will display a list of all the IP addresses for each NIC installed in your system so that you can select the IP Address that you want to use. In order for Advanced NMEA Data Logger to act as a server, the computer that it is running on must have at least one network interface card with an IP address assigned to it.
•If Advanced NMEA Data Logger will work as a server and your computer receives the IP address dynamically from a DHCP server, then you should ask your network administrator to assign a static IP address to your computer.
How to configure port parameters, you can read in the next "IP settings" chapter.
Advanced NMEA Data Logger can save data to a log file(s) without any changes (i.e., create raw binary log files) or write to log files depending on the parser module selected. In the first case, you can view the log file with any hex editor and use this data for further analysis and remaking. In the second case, you can view data with any text editor. You can find more information about log files in the "Log rotation" chapter.
You can watch the data in the data window (fig. 1). The data view is fully customizable. You can watch data in decimal, hexadecimal, or your format. How to customize data view you can read in the "Data view" chapter and how to customize program view you can read in the "Window view" chapter.
The data can be exported or transferred to one or more targets. The simplest way is to configure the log file rotation. However, it is small a part of all features of Advanced NMEA Data Logger. Advanced NMEA Data Logger has many additional modules (so-called plugins) that are appreciably extending possibilities of the logging software. You can download and install any module supported. Most modules are free of charge for our customers. How to install and configure modules you can read in the "Modules" chapter.
The program and their plugins generate many messages and write them to the list in the main window (fig. 1) and a protocol file that you can use for administration of the software. You can also configure types of system messages. More information about it you can read in the "Protocol and errors handling" chapter.
Data flow diagram
This diagram may help you to understand the flow of data within our software and a place of each module. The following chapters describe all plugin types.
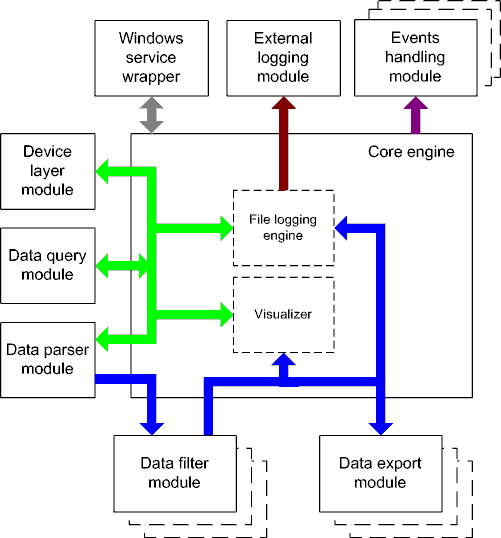
Fig. 3. Data flow diagram
History:
- The flow of binary data (RAW, unformatted data).
- The parsed data (formatted data). The data flow is separated into data packets and variables. Each data packet can be interpreted as a row, and each variable can be interpreted as a column.
Wires with other colors mark other relations with the unstructured data flow.
Work complete
The program saves all settings to the Windows registry when it stops working. All opened data sources will be automatically closed (unlocked, unallocated, or fried).
Useful advices
1. Look through hint helps on all window elements - it may help you to get a picture of this element's function.
2. You can change all program settings without restarting the program. To transfer settings to another computer, you can do the following:
1.Create a configuration backup from the "File" menu and restore it using the same menu.
2.Alternatively, export the registry node with all program settings. Start regedit.exe and export the following registry node:
on Windows x64
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\AGG Software\Advanced NMEA Data Logger
on Windows x32
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\AGG Software\Advanced NMEA Data Logger
3. On another computer import settings to the Windows registry.
Many main window elements have "hot" keys for quick access to its functions.
•Ctrl+S - analogs to click on "Start/Pause" button on the toolbar.
•Ctrl+C - analogs to click on "Clear" button on the toolbar.
•Ctrl+P - opens the window with the configuration settings.
•Ctrl+L - opens the window with the log file settings.
•Ctrl+W - allows you to configure the data view mode.
•Ctrl+R - shows the window with the program settings.
•Ctrl+E - shows the Windows 2000+ service settings.
•Ctrl+M - here you can configure data query plugins, data parser, and other plugins.
4. You can look at the summary statistic that contains summary about sent and received data, created files, etc. (View - Statistics)
5. You can save program settings to an INI file. It may help to install and use several copies of the program. You can make your choice from the "Options" menu.
6. The program window can display only the last 10 messages. The full program log file (if activated) you can open using the "File - View program protocol file" menu item.
Serial (COM) port
COM port is short for a serial communication port. Most serial communication software communicates with a computer through a communication port, and most IBM and IBM-compatible computers support up to four serial ports COM1, COM2, COM3, and COM4. Additional ports can be added by adding additional hardware.
Advanced NMEA Data Logger can manipulate with many serial ports at the same time (up to 255 serial ports).
You can open serial ports in Advanced NMEA Data Logger software in two modes:
1.Spy mode. In this mode the program monitor data flow on ports selected. In this mode, Advanced NMEA Data Logger intercepts all data exchange between any Windows application and external device.
2.Standard. In this mode, the program opens a serial port through Windows API functions, and read/write data from/to a serial port as a regular Windows application. In this mode opens a serial port with exclusive rights and other application will not have access to a serial port.
If one or more ports are configured already, then Advanced NMEA Data Logger is opening these ports and starting logging. If the port is opened successful, then the status bar in the main window displays a status of this port (fig. 1). However, before you should configure serial port parameters. The configuration can include one or more serial ports with identical settings. For example, if you have many identical devices, that connected to different serial ports, then you can specify port numbers in one configuration only. However, if you want to use a serial port with different settings, then you should create more than one configuration.
You can create the new configuration by clicking the "Plus" button in the main window (fig. 1) or through the "Options" menu. After you clicked the "Plus" button, the dialog window will be opened (fig. 5). The dialog window contains few sections with parameters. The "COM port" section is described in this chapter.
You can manage the configuration created with a drop-down menu near the "Plus" button (fig. 4).
Fig. 4. Access to the port configuration
The "COM port settings" tab contains indispensable settings of any serial port: baud rate, data bits, etc. You should configure it with the same values, that your external device uses for data exchange.
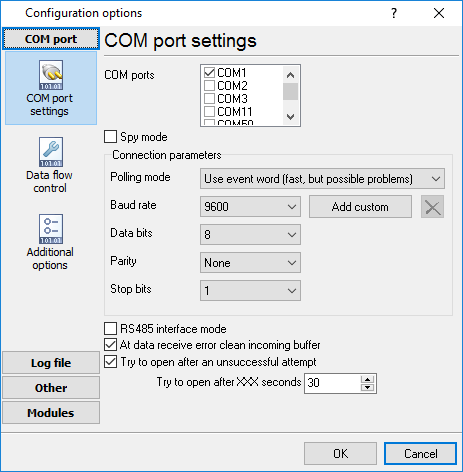
Fig. 5. COM port parameters
If you are logging data over RS-485 with an additional hardware converter and your converter doesn't support data direction auto-detection, then specify "RS485 interface mode". This option instructs Advanced NMEA Data Logger to set the RTS line at a low level while data receiving and vice versa. The serial port driver can detect errors while data receiving (for example, bad quality of a connection line). You can specify with the "At data receive error clean incoming buffer" option to ignore data blocks, that contain errors and clean an incoming buffer.
In some cases, the program can't open a serial port while starting (for example, the port is already used by other application). With the "Try to open after an unsuccessful attempt" option you can specify to try to open the serial port again after the interval specified. The program will try to open the serial port until an attempt will succeed.
The Windows communication API provides two methods to check for received data and line/modem status changes: API calls (polling) and an event word. The event word is maintained by the Windows communications driver. As data is received or line/modem status changes occur, the driver sets bits in the event word. The application can check the bits to determine if any communication events occurred. If so, the application can make the appropriate API call to clear the event word and retrieve the data or the new line/modem status values.
Windows also provides API calls to retrieve the same status information provided by the event word but the API calls are slower. Advanced NMEA Data Logger uses the event word by default for the fastest possible performance. Unfortunately, there is at least one communication driver (WRPI.DRV, included with some U.S. Robotics modems) that doesn't appear to support the event word. For this and similar drivers, select another mode before Advanced NMEA Data Logger will receive data.
If you want to rise data transmit adequacy you can use hardware and/or software data flow control (fig. 6). When using hardware data flow control are used some lines (wires) of connecting cable. Depending on used lines, you must configure checks against corresponding fields.
Hardware flow control
When the hardware flow control options are an empty, as they are by default, there is no hardware flow control. The options can be combined to enable hardware flow control.
"Receive flow control" stops a remote device from transmitting while the local input buffer is too full. "Transmit flow control" stops the local device from transmitting while the remote input buffer is too full.
Receive flow control is enabled by including the "Use RTS" and/or "Use DTR" elements in the options. When enabled, the corresponding modem control signals (RTS and/or DTR) are lowered when the input buffer reaches the 90% size of the buffer. The remote must recognize these signals and stop sending data while they are held low.
As the application processes received characters, buffer usage eventually drops below the 10% size of the buffer. At that point, the corresponding modem control signals are raised again. The remote must recognize these signals and start sending data again.
Transmit flow control is enabled by including the "Require CTS" and/or "Require DSR" elements in the options. With one or both of these options enabled, the Windows communications driver doesn't transmit data unless the remote device is providing the corresponding modem status signal (CTS and/or DSR). The remote must raise and lower these signals when needed to control the flow of transmitted characters.
Note that flow control using RTS and CTS is much more common than flow control using DTR and DSR.
Software flow control
This routine turns on one or both aspects of automatic software flow control based on the value assigned to the property.
"Receive flow control" stops a remote device from transmitting while the local receive buffer is too full. "Transmit flow control" stops the local device from transmitting while the remote receive buffer is too full.
Receive flow control is enabled by assigning "On receiving" or "Both" to the "Type" property. When enabled, a Xoff character is sent when the input buffer reaches the 10% level of of the buffer size. The remote must recognize this character and stop sending data after it is received.
As the application processes received characters, buffer usage eventually drops below the 10% level of the buffer. At that point, a Xon character is sent. The remote must recognize this character and start sending data again.
Transmit flow control is enabled by assigning "On transmitting" or "Both" to the "Type" property. The 10% and 90% size of the buffer are not used in this case. When transmit flow control is enabled, the communications driver stops transmitting whenever it receives a Xoff character. The driver does not start transmitting again until it receives a Xon character, or the user sets software flow control to "None'.
Software data flow control can be configured on receive, transmit, or both modes, but so as the great number of a device doesn't need data sending, select the "On receive" control mode. In case of activation of data transmit control, a remote object (your device) can send special codes, signalizing about data transmit stop or start. On default, received from device character 0x11 Hex signalizes to COM port driver to start data receive and character 0x13 Hex - to stop data receiving from a device.
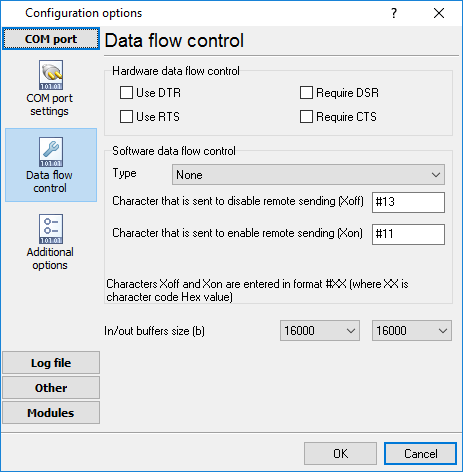
Fig. 6. Data flow control
Spy mode
In this mode, Advanced NMEA Data Logger doesn't send and receive any data, and only spies on data exchange, made by other programs. You should enable the "Spy mode" checkbox.
Also, you must start the logger before any other program that can use the selected COM port.
After this, the logger will capture and show data exchange over the selected COM port in the main window.
Note: You must close the program you monitor, before closing Advanced NMEA Data Logger.
Serial data transfer errors
Line errors can occur during data exchange and displayed in the main program window in the status bar.
UART receiver parity error - occurs if you configured an invalid parity type.
UART receiver overrun,
UART receiver framing error - occurs if you configured an invalid number of stop or data bits.
Transmit timeout waiting for CTS,
Transmit timeout waiting for DSR,
Transmit timeout waiting for RLSD - occurs if you configured invalid hardware flow control, or your serial interface cable isn't wired for hardware flow control.
Transmit queue is full - occurs if Advanced NMEA Data Logger can't send data to a remote device.
Break - Break signal is received.
Port restart
You can also set the program to initiate the serial interface at the specified time. On some old versions of the Windows NT operating system it could help to avoid the loss of data when the program has been working for a long time without restarting. Please use the "Additional options" tab (fig. 7)
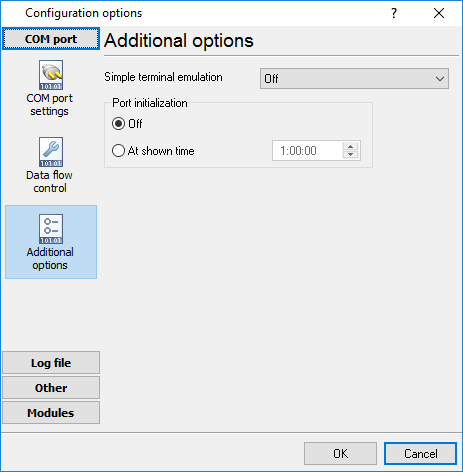
Fig. 7. Additional options
Here you can also select the terminal emulation mode. In this mode, the program will remove or interpret some special terminal sequences automatically.
TCP/IP settings
UDP vs. TCP
The most commonly used network protocols today are TCP (Transport Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). TCP is a proven and reliable protocol, and probably the most widely implemented protocol in use on IP networks today. However, TCP has a lot of overhead and payload issues, and can sometimes be ‘too-reliable’ or robust for many applications. In fact, when used as transport, for many serial-based applications TCP can hinder reliable communications. In contrast, UDP is a much simpler protocol and is being used more frequently today - particularly in areas where bandwidth or throughput is constrained. An example is the predominant use of UDP for transport of wireless data applications.
UDP is first a connectionless protocol. Like TCP, UDP runs on top of IP networks. But unlike TCP, UDP does little to help with transport delivery or error recovery. Instead, it offers a direct way to send and receive packets, letting the software application manage things like error recovery and data retransmission. Once primarily used for broadcasting small messages, UDP is now used for everything from browsers to Instant Messaging, Video, and Voice over IP applications.
While a powerful tool, the downside to using UDP is that there is not ‘connection’ report to know that you have end-to-end connectivity. This often makes detecting whether or not a packet is ‘making it’ from one place to another quite a hassle.
Client vs Server
Advanced NMEA Data Logger can be configured to log data from as many ports that you like simultaneously on a single computer. The program allows you to create multiple configurations for this task. Each configuration may contain different settings for each TCP/IP port. Each configuration has a set of TCP/IP parameters that are described below.
Each port configuration (i.e. TCP/IP connection) in Advanced NMEA Data Logger can act as:
| 1. | Client. You will need to specify the remote host IP address and the port number for the TCP/IP server that you want to connect to. The IP address that you specify in Advanced NMEA Data Logger when configuring it as a client may also be either a URL or the name of a computer located on your network. For example, if you want to connect to a computer named "Plant1", you can simply enter "Plant1" for the IP address instead of the actual IP address. If you are configuring Advanced NMEA Data Logger as a client and your network is set up to assign IP addresses dynamically to each workstation, then you may need to use the name of the computer that you want to connect to instead of an actual IP address to guarantee a connection. |
| 2. | Server. In this mode you should specify the IP address of the local computer will be used and you only need to specify the port number that you would like to use. If your computer has more than one network interface card (NIC) then Advanced NMEA Data Logger will display a list of all the IP addresses for each NIC installed in your system so that you can select the IP Address that you want to use. In order for Advanced NMEA Data Logger to act as a server, the computer that it is running on must have at least one network interface card with an IP address assigned to it. In Microsoft Windows, the TCP/IP protocol can be configured to automatically obtain an IP address from a host computer. It means that your computer may not have an IP address until it is connected to a network server or a host computer. You may need to contact your network administrator to assign an IP address to your computer if you wish to configure a TCP/IP server connection. This is done in the network settings for the TCP/IP protocol in your control panel. |
After you enter the parameters that you would like to use, you must click the "OK" button to establish a connection between Advanced NMEA Data Logger and the TCP/IP port. If the current port configuration is set up as a client, it will immediately try to establish a connection to the specified remote server. If the server is not available, Advanced NMEA Data Logger will continually try to establish the connection until it is successful. If the port configuration is set up as a server, it will listen on the specified port until a client establishes a connection to it.
If one or more ports are configured already, then Advanced NMEA Data Logger is opening these ports and starting logging. If the port is opened successful, then the status bar in the main window displays a status of this port (fig. 1). However, before you should configure port parameters that are described below.
You can create the new configuration by clicking the "Plus" button in the main window (fig. 1) or through the "Options" menu. After you clicked the "Plus" button, the dialog window will be opened (fig. 9). The dialog window contains few sections with parameters. The "IP settings" section is described in this chapter.
To log data from more than one TCP/IP connection, you would create and configure multiple port configurations. You can manage the configuration created with a drop-down menu near the "Plus" button (fig. 8).
Fig. 8. Access to the port configuration
The "IP settings" tab contains indispensable settings of any TCP/IP port: IP address and port.
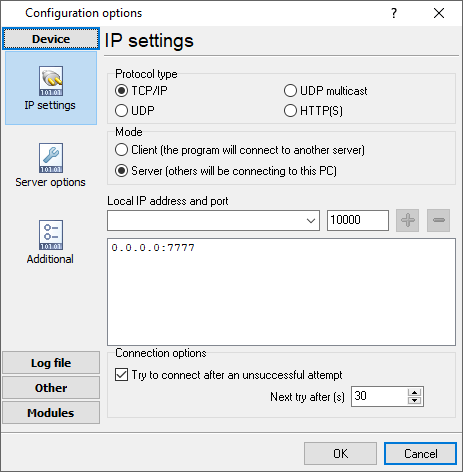
Fig. 9. TCP/IP parameters
Port
In addition to the IP address, you should specify how to connect to a remote machine. Our software can be thought of as a trunk line with thousands of individual lines (the ports) which are used to connect machines. Some ports are considered well-known ports. For example, the port typically used for network mail systems (SMTP) is port 25, the telnet port is port 23, the network news server port (NNTP) is typically port 119, and so on. To see a list of well-known ports, inspect the SERVICES file in the Windows directory (for Windows NT it is in the WINNT\SYSTEM32\DRIVERS\ETC directory). The SERVICES file is a text file used by Advanced NMEA Data Logger to perform port lookups (which return the service name for the specified port) and port name lookups (which return the port number for the specified service name). You can open this file in any text editor to see a list of port numbers, and their corresponding service names. While these well-known ports are not set in stone, they are traditional and their use should be reserved for the service which they represent. When writing network applications, you should select a port number that is not likely to be duplicated by other applications on your network. In most cases, you can choose a port number other than any of the well-known port numbers.
The IP address and port number are used in combination to create a socket. A socket is first created and then is used to establish a connection between two computers. How the socket is used depends on whether the application is a client or a server. If an application is a server, it creates the socket, opens it, and then listens on that socket for computers trying to establish a connection. At this point, the server is in a polling loop listening and waiting for a possible connection. A client application, on the other hand, creates a socket using the IP address of a particular server and the port number that the server is known to be listening on. The client then uses the socket to attempt to connect to the server. When the server hears the connection attempt, it wakes up and decides whether or not to accept the connection. Usually, this is done by examining the IP address of the client and comparing it to a list of known IP addresses (some servers don’t discriminate and accept all connections). If the connection is accepted, the client and server begin communicating, and data is transmitted.
Connection options
If the remote server (in the client mode) or local network interface (in the server mode) is not available and the "Try to connect after unsuccessful attempt" options is True, then Advanced NMEA Data Logger will continually try to establish the connection until it is successful. The program will try to establish the connection every N seconds that you can specify in the "Next try after XXX seconds" field.
Server options - Allowed IP addresses
This option is active in the server mode and allows you to enter one or more IP addresses that have access to the server. The server refuses connections from any other IP address. This option is very useful if you transfer your data over an Internet connection or your server computer is connected to a big corporate network. You can specify multiple addresses - one per row. If you do not specify any address here, then Advanced NMEA Data Logger will accept connections from all IP addresses.
You can also use a mask in IP addresses like: 192.255.255.255
All parts of the IP address with 255 will be ignored (not tested).
You can also use special characters "+" and "-" before an IP address. IP addresses with these prefixes should be first in the list.
"+" - allow all connections from this address.
"-" - block all connections from this address.
Example:
+192.168.1.255
+127.255.255.255
-1.1.1.1
Firewall settings
After you install Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2), our Advanced NMEA Data Logger may not seem to work. Windows Firewall, enabled by default, blocks unsolicited access to your computer via the network and may be blocking the normal operation of the program. To provide increased security to Windows XP users, Windows Firewall blocks unsolicited connections to your computer. When Windows Firewall detects incoming network traffic that it does not recognize, a Security Alert dialog box appears. The security alert dialog box looks like this:
Fig. 10. Firewall alert
The dialog box includes the following buttons:
•Unblock this program.
•Keep Blocking this program.
•Keep blocking this program, but Ask Me Later.
For our program to function properly, you must unblock the program by clicking the Unblock button. Unblocking allows Windows XP SP2 to allow the program to continue to work by adding it as an exception to your Windows Firewall configuration. Exceptions are specific programs and processes that you allow bypassing the firewall. After you add a program as an exception, you no longer receive the security alert. If you choose to continue blocking the program, certain functions will be disabled.
Note: If you are using another firewall software, then please, refer to a firewall manual for corresponding settings.
Limitations
The specific limit of connections is dependent on how much physical memory your server has and how busy the connections are:
The Memory Factor: According to Microsoft, the WinNT and successor kernels allocate sockets out of the non-paged memory pool. (That is, the memory that cannot be swapped to the page file by the virtual memory subsystem.) The size of this pool is necessarily fixed, and is dependent on the amount of physical memory in the system. On Intel x86 machines, the non-paged memory pool stops growing at 1/8 the size of physical memory, with a hard maximum of 128 megabytes for Windows NT 4.0, and 256 megabytes for Windows 2000. Thus, for NT 4, the size of the non-paged pool stops increasing once the machine has 1 GB of physical memory. On Win2K, you hit the wall at 2 GB.
The "Busy-ness" Factor: The amount of data associated with each socket varies depending on how that socket's used, but the minimum size is around 2 KB. Overlapped I/O buffers also eat into the non-paged pool, in blocks of 4 KB. (4 KB is the x86's memory management unit's page size.) Thus, a simplistic application that's regularly sending and receiving on a socket will tie up at least 10 KB of non-pageable memory.
The Win32 event mechanism (e.g., WaitForMultipleObjects()) can only wait on 64 event objects at a time. Winsock 2 provides the WSAEventSelect() function which lets you use Win32's event mechanism to wait for events on sockets. Because it uses Win32's event mechanism, you can only wait for events on 64 sockets at a time. If you want to wait on more than 64 Winsock event objects at a time, you need to use multiple threads, each waiting on no more than 64 of the sockets.
If you have more than 64 connection at a time, then we recommend creating multiple configurations in our software (the "Green Plus" button). Each configuration will use different port number and will run in a different thread. This change will allow decreasing the influence of Windows limitations.
Additional parameters
The "Additional" tab contains additional settings of a TCP/IP or UDP connection (fig. 11).
Simple terminal emulation - the program realizes the simple implementation of some terminal protocols. If this emulation is enabled, then the program will process some special commands and character sequences.
Optimize for small data packets - if the logger sends or receives data packets with size less than 1500 bytes, it is recommended to enable this option.
Following options are effective only in the "TCP/IP server" mode:
Limit of simultaneous connections - you can define the number of clients that can connect to the server at the same time. It allows optimizing a server load with a large number of TCP clients.
Disconnect inactive clients after (s) - if a client is connected, but didn't send or receive any data within the specified time, then the connection with this client will be closed. If you will specify "-1," then the clients will not be disconnected.
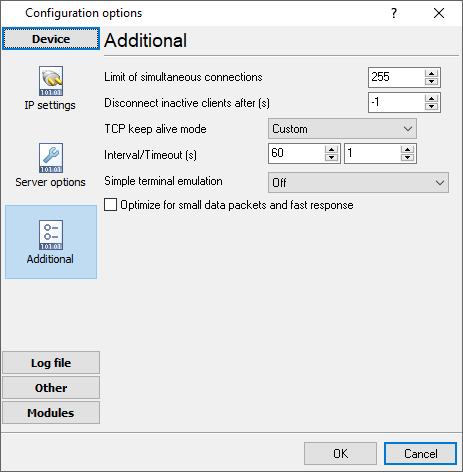
Fig. 11. Additional parameters
Following options are effective only in the TCP/IP server or client modes:
TCP keep-alive mode
A TCP keep-alive packet is a short packet which is sent periodically by the OS to keep the connection alive. The connection stays alive because those packets and their replies generate small traffic on the connection when the application is idle.
Keep-alives can be used to verify that the computer at the remote end of a connection is still available.
It is simply an ACK with the sequence number set to one less than the current sequence number for the connection. A host receiving one of these ACKs responds with an ACK for the current sequence number.
TCP keep-alive can be sent once every KeepAliveTime (defaults to 7,200,000 milliseconds or two hours) if no other data or higher-level keep-alive have been carried over the TCP connection. If there is no response to a keep-alive, it is repeated once every KeepAliveInterval seconds. KeepAliveInterval defaults to 1 second. Some (buggy) routers may not handle keep-alive packets properly.
Our software supports three modes of keep-alive (fig. 11):
1. Off - the program doesn't use the keep-alive feature at all. You can disable it if your network is very stable or your routers do not support it.
2. System - the program will use the keep-alive feature, but use system values of KeepAliveTime and KeepAliveInterval. These values are stored in the following registry branch:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters]
KeepAliveTime (32-bit number) = milliseconds
KeepAliveInterval (32-bit number) = milliseconds
3. Custom - the program will use keep-alive, but you can specify your values of KeepAliveTime and KeepAliveInterval, that are more applicable for your network and system. Note: in our software, you should define these values in seconds.
Note: Some routers may not allow keep-alive TCP packets. In this case, the "keep-alive" function will not work.
Data view change
The data in the main window (fig.1) can be displayed in two modes (fig. 12):
| 1. | The data can be displayed before processing. Before processing the data I fully comply with that has been read. |
| 2. | The data can be displayed after processing. After processing the data can be modified depending on the parser. |
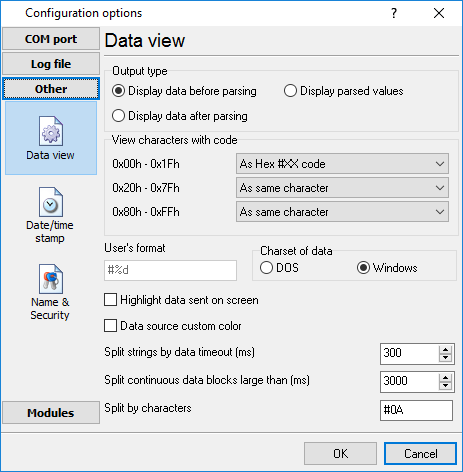
Fig. 12. Data view
Data view settings, that can be configured on the "Data view" tab:
1.View characters with code - the program can interpret and decode bytes as characters. You can select decoding mode for each range of character codes. If the range doesn't have the corresponding character, that's why these data can be displayed only in hexadecimal and decimal code.
2.You can set up the user's format to display a data byte. The directive %d shows to display a decimal code, the directive %x - hex code. You can set any framing characters before/after the user format.
3.Highlight data sent on screen - a string with sent data will be highlighted by the selected color.
4.Character set - allows you to define the character set of incoming data. Windows - Windows ANSI character set, DOS - OEM character set.
5.Data source custom color - if you've created several configurations then you can define a custom color for each data source that allows you to distinguish data flows on the "All data" page in the main window.
6.Split strings by data timeout - this option allows visually splitting data packets in the program window. Data packets that will be received after the specified interval will be shown on a new line. If this value is set to 0, then data packets will not be split.
7.Split continuous data blocks large than - this option allows visually splitting continuous data flow in the program window. The program will show data on a new line if continuous data is longer than the specified number of bytes.
8.Split by characters - this option allows to visually splitting continuous data flow in the program window using the specified symbols. For example (fig. 12), the program will use a character with the 0Ah hexadecimal code that is equal to the "LF" ASCII code.
Date/time configuration
This group of options (fig. 13) allows you to configure how timestamps appear in the log file and on the screen. You can configure the stamp format in the program options.
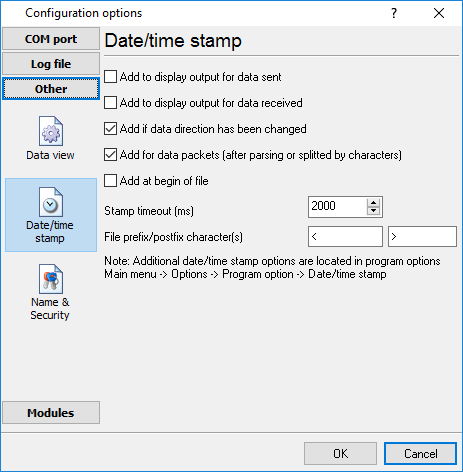
Fig. 13. Time stamp configuration
Add to display output for data sent - the time stamp will be added for the sent data displayed on the screen. The stamp will be added according to the timeout (if the data flow is uninterrupted) or when a data packet is sent.
Add to display output for data received - the same but for the received data.
Add if data direction has been changed - if the program is sending and receiving data, the time stamp will be also added when the data transfer direction changes (sending/receiving).
Add for data packets - if the data is displayed after it is processed, the stamp will be added to each processed data packet.
Add at begin of file - the stamp will be added at the beginning of every new log file.
Stamp timeout - if the data flow is uninterrupted, the stamp will be added regularly at the interval specified in milliseconds.
File prefix/postfix character(s) - the program will use these characters instead of those specified in the program options while writing data to a file. For example, it allows you to add the new line character or another sequence of characters before or after the stamp. Example: >#0D#0A
Name and security
This group of options (fig. 14) allows you to configure the following parameters:
Friendly name - this name will be added before the port number or the data source in the drop-down list in the main window of the program. It allows you to describe the data source.
Start logging automatically - if this option is enabled the program will start receiving and logging data automatically when it is launched.
The "Security" option group allows you to protect user operations in this particular configuration with a password. You can specify advanced security options applied to the entire program in the program options.
Ask password before start and stop - the password will be required when the user clicks the "Start/Pause" button in the main window of the program.
Ask password before configuration edit - the password will be required when the user tries to open the Configuration options dialog box.
Fig. 14. Name and security
Log rotation
The main function of Advanced NMEA Data Logger is logging data to a file (so-called, log file). The "Log rotation" tab has a rich set of options for it. (fig. 15).
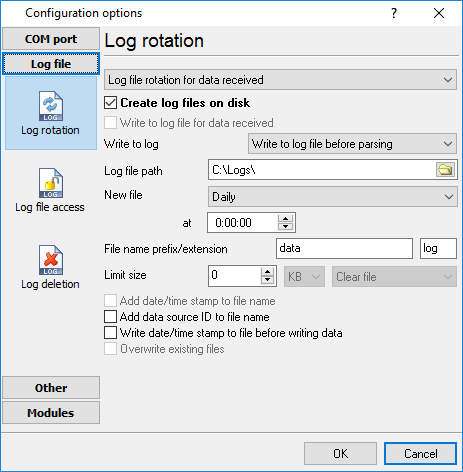
Fig. 15. Log-file forming modes
First of all, select log file what you can configure:
•Log file for data received - all data received will be saved using these settings.
•Log file for data sent - these settings will be used to save sent data. If you want to save data to the same file, as data received, then select the "Log file rotation for data sent" option from the list and enable two options: "Create log files on disk" and "Write to log for data received." Of course, you should configure a log rotation for data received before.
Set the "Create log file on disk" option to the checked state. Then you can set path to a folder, where files will be created with the help of a dialog window, which will be showed up after clicking a button with the "Folder" picture. You should select a necessary folder in the dialog window and click the "OK" button.
Log file path - the full path to a local or network folder, where the program will create new log files. The network path should be specified as: \\COMPUTER NAME\Folder\
Note: If the program works with network files, it greatly increases data flow through your network and decreases writing speed. Please, consider creating small log files. If your incoming data flow is fast, you may create log files locally. Later, you may sync a local folder with a remote folder using any 3rd party utility.
A log file name can be stamped with date and time. In this case, a new log file is created periodically. The format of a timestamp depends on the selected period. For instance, if the "File name prefix" field is set to "sample," the "File extension" field to "log," and the "File name format" option is "Daily," then each log file created will have the format "sampleYYYYMMDD.log". On March 21st, 2003, the log file will be "sample20030321.log". Please, note, that the final extension (after the final period), remains at the end of the file name.
Write to log - the option allows you to select when the program writes data to a log file. This feature is disabled in some loggers, and if the parser plugin is not available.
•Before parsing - the program saves all incoming data without any modifications. If an external device sends binary data, the logger will create binary files.
•After parsing - the program saves data after parsing. Generally, it is a parsed data packet.
•After filtering - the program saves data after all filter plugins. The logger saves the content of the "FULL_DATA_PACKET" variable. A filter plugin may transform or fully change the variable. If you do not use any filter plugin, then this mode works as the previous.
•Screen content - the program saves data to a log file as you see it in the main window. Generally, it is text content; therefore, the program creates a text log file.
The log rotation mode is defined by the following key parameters:
•File name prefix - the text string, which will be added at file name beginning. The prefix may contain special placeholders like {NAME}. If you create log files before parsing the NAME can be any date formatting values below. For example: "data{YYYY}_{MM}_{DD}" returns a prefix like "data2019_01_01". If you create log files after parsing or filtering, you may use any parser variable. Then the file name may depend on some value in your incoming data.
•File name extension - the text string, which will be a file extension (characters after the dot).
Limit size - the "Limit size" field specifies the maximum size in kilobytes of any log file. If you specify the zero file size, then the file size is not limited.
You may select from the following modes:
1.Clear file - if the log file size will exceed the limit specified, then the log file content will be deleted, and file filling will start from the beginning.
2.Rename old - if the log file size will exceed the limit specified, then the existing log file will be renamed.
3.Shift (no threshold) - the older data over the limit specified will be removed from the log file.
4.Shift (with threshold) - in this mode the program will wait when the file size will exceed the limit specified + the threshold value. After this, the older data over the limit specified will be removed from the log file.
If the program continuously works for a long time, it is possible that the log file will have a large size and this file will be inconvenient for looking and analyzing. Therefore, there is the possibility to create files in dependence with the time on a computer. You can select one variant predefined or set up a new one:
•Daily - the file will be created with a name containing a prefix, and date in format DDMMYYYY, where DD is two-digit day sign, MM is two-digit month sign, and YYYY is four digits of the current year. The filename extension will be added at the end of the file.
•Monthly - the file will be created with a name containing a prefix, and date in MMYYYY format. The filename extension will be added at the end of the file.
•Each data packet in different file - in this mode, the program splits data flow to a different file. In this mode you should configure the parser or the program will split a data by timeout about 300 milliseconds.
•Don't create new file - in this mode, the program will write all data to one file. It is recommended for a small data flow. Otherwise, your log file will be too big, and a performance of the program will fall down.
•User's format - a file will be created with a name containing a prefix and date in showed by you format (for example, DDMMYYYY). The filename extension will be added at the end of the file. The file may not contain format signs, then file name will be constant. You should not use characters, that the OS doesn't allow in a file name, such as "/,\.*,?" and some others.
•Weekly - create a new file every week. The file name will contain a week number.
•After data timeout - the program will create a new file if the program didn't receive any data at the specified interval.
•Hourly - the file will be created with a name containing a prefix, and date in format YYYYMMDDHH, where HH is two-digit hour sign, DD is two-digit day sign, MM is two-digit month sign and YYYY is four digits of the current year. The filename extension will be added at the end of the file.
•Constantly named file - the current log file will have a constant name. When creating a new file, the existing log file will be saved using the new file name that will contain a date and time stamp.
If you need to create a new log file under more complex conditions, then you can try the additional "Scheduler & Hotkeys" plugin. You should download and install it separately.
Date and time formatting codes:
D - a day number (1-31).
DD - a day number with a leading zero (01-31).
DDD - a day of the week in the text form (Mon-Sat), according to the regional settings on this computer.
DDDD - a day of the week in the full text form (Monday-Saturday), according to the regional settings on this computer.
M - a month number (1-12).
MM - a month with a leading zero (01-12).
MMM - a month name in the text form (Jan-Dec), according to the regional settings on this computer.
MMMM - the full month name (January- December).
YY - last two digits of the year (00-99).
YYYY - the full year number (0000-9999).
H - the hour number (0-23).
HH - the hour number with a leading zero (00-23).
N - minutes (0-59)
NN - minutes with a leading zero (00-59).
S - seconds (0-59).
SS - seconds with a leading zero (00-59).
W - ISO week number (Monday is the start of the week).
WW - week number (the start of the week is defined in System - Regional settings).
To insert arbitrary text or a symbol into a date or time format, and to prevent it from being accidentally replaced with some value, you need to use quotes:
YYYY"/"MM"/"DD - 2023/01/01
YYYY"/"MM"/"DD"T"HH:NN:SS - 2023/01/01THH:NN:SS
Addinal parameters
CLIENTID - the unique client or data source ID (in some data loggers).
CLIENTNAME - the unique client or data source name (in some data loggers).
Example: You want to create a log file every hour. It is desired that file name starts from "sample_log" and the file extension "txt".
Answer: set file prefix = sample_log_, file extension= txt (without dot!). In file name format show HHDDMMYYYY. Now the file will be created every hour. Naturally, you can set any formatting characters combination, described higher.
If you want to access to a log file while the program work, then you should configure access mode settings for the log file in the next chapter.
Add date/time stamp to file name - this option is available for modes #4 and #7 and allows adding date and time to the file name.
Add data source ID to file name - if this option is activated, then the program will append the data source name at the beginning of the file name, for example, COM1-sample20030321.log.
Write data/time stamp to file before writing data - if this option is activated, then the program will write a date/time stamp to a file before each data portion.
Overwrite existing files - this option is available for modes #4 and #7 and allows you to delete an existing log file before creating a new log file.
Log file access
During work can be such situations, when it is necessary to get access to a file with current data (current log file) from other applications (for example, for data processing). However, while you are accessing the current log file Advanced NMEA Data Logger can't write data to a log file and all data at this moment will be lost. We recommend using a temporary file for data storage. It is the safest way. (fig. 16).
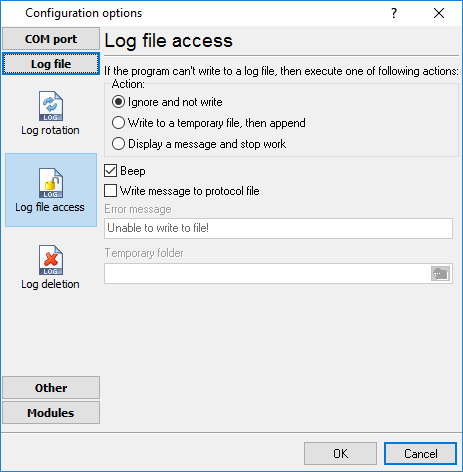
Fig. 16. File access mode.
You can select one from the following variants:
•Ignore and not write - in this mode, the program stop writing to a log file until it is locked. Therefore, data will be lost.
•Write to a temporary file, then append - a temporary file will be created, to which writing will be done. After access to the current file will be got, temporary file content will be added to the end of the main file. However, mind that if file has a timestamp in the name, there can be a situation when the program copies the content of a temporary file to a new log file, for the next time.
•Display a message and stop work - data will be lost until the dialog window is closed.
You can define your message text, which will be displayed at writing error to a log file. The sound signal can be on for an additional indication. You can also enable writing a message to a protocol file.
Log deletion
The deletion of files (fig. 17) will help you to avoid stuffing your hard disk with needless information. Log files can be deleted either depending on the time of storing or when the maximal number of files is exceeded.
When deleting files by the time of their storage, the files that were modified last time before the specified period are deleted.
When controlling the number of files, the files with the oldest modification dates are deleted first.
You can select both variants of file deletion. In that case, files will be deleted when either of the conditions is true.
Fig. 17. Log deletion
Introduction & setup
To extend program functionality, we implemented plugin modules. The module structure lets you to reduce your program size and purchase costs (you pay only functionality, which you need).
Advanced NMEA Data Logger supports a few types of modules (fig. 18 - 20):
•Data query - transmits queries or commands out the data source to control or query your devices.
•Data parser - the data parser allows you to parse, filter, and format data from your data sources. Some of the advanced features of the parser are the ability to work with raw binary or hex data.
•Data filter - data filters allow you to filter your data and modify a value of parser variables.
•Data export (fig. 20) - Advanced NMEA Data Logger has many modules and method for passing data to other applications, for example, there are modules for various databases, file formats (CSV, XML), data interfaces (OPC, DDE, MQTT), and many others.
•Events handling (fig. 21) - these plugins are used to handle events generated by the Advanced NMEA Data Logger software. Once an event occurs (for example, "Data source is opened" or "Configuration changed"), the plugin creates a text message using the specified template, sends a notification, does some actions, executes a program or a script, etc. The form of the notification or actions depends on the plugin settings.
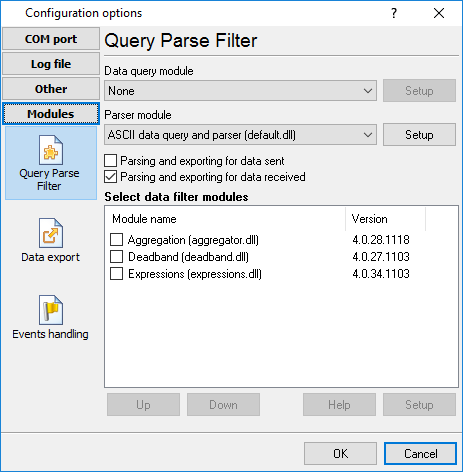
Fig. 18. Activating plugins
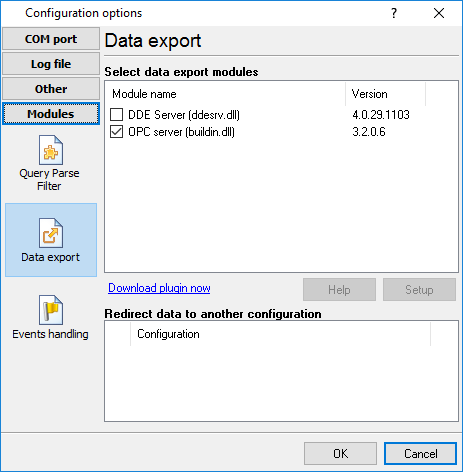
Fig. 19. Activating data export plugins
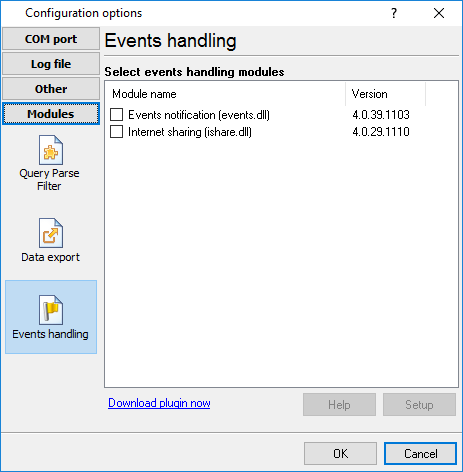
Fig. 20. Activating events handling plugins
You can parse and export data sent and received. By default, only data received will be parsed.
Installation
You can easily install a new module. Usually, you should start the installation file and click the "Next" button for a few times. The installation wizard will detect a place of your Advanced NMEA Data Logger software and place a plugin module and all distributive files to the "Plugins" folder, which is in the program folder (by default X:\\Program Files\Advanced NMEA Data Logger\Plugins).
After the program restart, a module will be loaded and initialized. If the module is supported by our software, the module name will appear in the modules list. Most modules require additional settings. If you want to configure the plugin module, click the "Setup" button near it. If you selected the module and the "Setup" button is not active, then the module doesn't have additional settings and can work without additional settings. Please, read a user's manual of the corresponding plugin for additional information.
Configuration steps
1.Select and configure a query module. You may use a module of this type if you need to send some data to your device (for example, initialization strings or request strings).
2.Select and configure a parser module. This step is necessary because filter and export modules can use parsed data only. If you didn't select the parser module, then you can't configure the data filter and data export modules.
3.Activate and configure data export modules. You can select one or more modules simultaneously. The program will use selected modules simultaneously. Please, note, the program can' use the data export module, if you didn't configure the parser module.
4.Activate and configure event modules. You can select one or more modules simultaneously.
OPC server
Advanced NMEA Data Logger has an internal OPC server. It means that any OPC compatible client application can get data from Advanced NMEA Data Logger without any additional software. To connect to the OPC server, you need the server ID and name (fig. 21). Before using the OPC server on your computer, you should download and install the OPC Core Components Redistributable from www.opcfoundation.org (registration required).
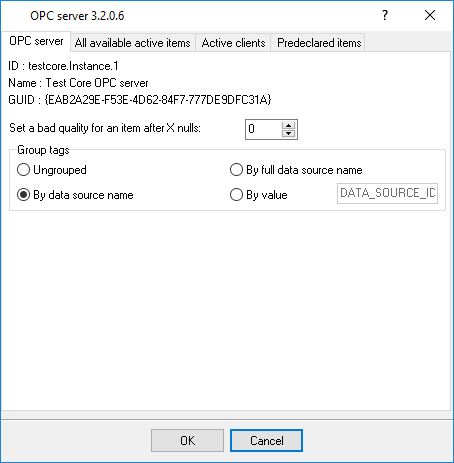
Fig. 21. OPC server parameters
Advanced NMEA Data Logger parses all incoming data to one or more variables, and an OPC client gets it (fig. 22). After connecting to the OPC server, you will get a list of all variables.
Fig. 22. OPC server active items
Clients activity is showed on the "Active clients" tab. The top node is client, below is a group of items and connected items. By double-clicking, you can get detailed information about each node.
Fig. 23. OPC server clients
Advanced NMEA Data Logger creates new variables at "on-the-fly" mode. The Advanced NMEA Data Logger starts without any variables and gets it only after first data had been received. If your client OPC will connect to the OPC server before than data had been processed, then it will get an empty list of variables, and your OPC client should poll the OPC server for updating list of variables. If your OPC client doesn't allow it, then you can predefine all variables (fig. 24). In this case, the OPC server will create these variables with empty values, immediate after starting, and your OPC client will get these names while connecting.
Fig. 24. OPC server pre-declaration
Introduction
The National Marine Electronics Association (NMEA) has developed a specification that defines the interface between various pieces of marine electronic equipment. An NMEA standard defines an electrical interface and data protocol for communications between marine instrumentation. (They may also have standards for other things.)
NMEA 0183 devices are designated as either talkers or listeners (with some devices being both), employing an asynchronous serial interface with the following parameters: Baud rate: 4800, Number of data bits: 8 (bit 7 is 0), Stop bits: 1 (or more), Parity: none, Handshake: none. NMEA 0183 allows a single talker and several listeners on one circuit.
GPS receiver communication is defined within this specification. Most computer programs that provide real time position information understand and expect data to be in NMEA format. This data includes the complete PVT (position, velocity, time) solution computed by the GPS receiver. The idea of NMEA is to send a line of data called a sentence that is totally self contained and independent from other sentences. There are standard sentences for each device category and there is also the ability to define proprietary sentences for use by the individual company. All of the standard sentences have a two letter prefix that defines the device that uses that sentence type. (For GPS receivers the prefix is GP.) which is followed by a three letter sequence that defines the sentence contents. In addition NMEA permits hardware manufactures to define their own proprietary sentences for whatever purpose they see fit. All proprietary sentences begin with the letter P and are followed with 3 letters that identifies the manufacturer controlling that sentence. For example a Garmin sentence would start with PGRM and Magellan would begin with PMGN.
Our module parse each sentence begins with a '$' and ends with CRLF (a carriage return/line feed sequence). The data is contained within this single line with data items separated by commas. The data itself is just ASCII text and may extend over multiple sentences in certain specialized instances but is normally fully contained in one variable length sentence. The data may vary in the amount of precision contained in the message. For example time might be indicated to decimal parts of a second or location may be show with 3 or even 4 digits after the decimal point. There is a provision for a checksum at the end of each sentence which may or may not be checked by the unit that reads the data. The checksum field consists of a '*' and two hex digits.
Our parser module splits all data to variables and this variables can be used in data export modules.
Common parameters
These parameters are used for data parsing (fig. 25).
1.Add date/time stamp to each sentence parsed - the parser will add an additional stamp value to other values, that the parser will extract from a data block;
2.Add serial port number to each sentence parsed - the parser will add an additional value with serial port number, that received this data block. You can use it in a multi port configuration, for identifying sentences from different serial ports.
3.Verify sentence checksum if available - the parser will calculate a checksum and verify it for each sentence that will contain '*' characters at the end of sentence:
Sentence example:
GPGGA,123519,4807.038,N,01131.000,E,1,08,0.9,545.4,M,46.9,M,,*47
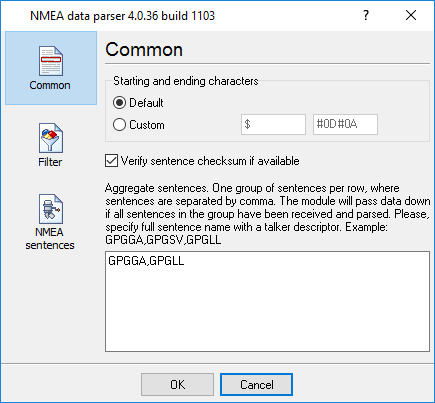
Fig. 25 Common parameters
Aggregate sentences
This option is very useful if your talker sends more than one sentence and you want to save data to a file at single row. You can aggregate two or more sentences and data of these sentences will be send to data export modules at same moment with one date time stamp. If you'll specify sentence names then the module will store all data in a temporary buffer, while all sentences isn't received. When all data is received the module sends data to a data export module, clears the buffer and starts waiting for new data.
You can specify one or more different aggregate groups. Simply add sentence name to different rows. Sentences in the row should be separated by comma and a sentence should contain a talker name.
NMEA sentences parser
If you want to export to any target, then you should configure a parser module. The ASCII data parser allows you to extract data from data flow, that contains a ASCII characters. The parser module splits data flow to data block and extracts data values from each data block. On the "sentence" tab (fig. 5.3.2) you should specify sentences, that the parser will parse. Other sentences will be ignored.
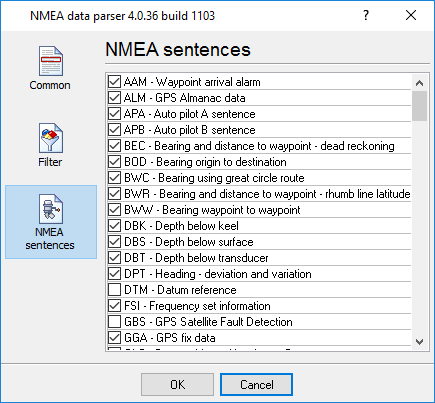
Fig. 5.3.2 NMEA sentences
The full list of supported sentences and variables that parsed from each sentence is listed here.
Our software create variables with following types:
•String - Characters array with length from 1 to 65535 characters;
•Boolean - Logical value (True/False) - 0 or 1;
•Float - Real number - value range: -2.9 x 10^-39 .. 1.7 x 10^38
•Integer - Integer value: -2147483648..2147483647;
•DateTime - Date and time.
Note: Our modules doesn't support Time and Date data types. Therefore time variables, that exists in a sentence contains current date, but with time from the sentence.
Supported talkers
AG - Autopilot - General
AP - Autopilot - Magnetic
CD - Communications – Digital Selective Calling (DSC)
CR - Communications – Receiver / Beacon Receiver
CS - Communications – Satellite
CT - Communications – Radio-Telephone (MF/HF)
CV - Communications – Radio-Telephone (VHF)
CX - Communications – Scanning Receiver
DF - Direction Finder
EC - Electronic Chart Display & Information System (ECDIS)
EP - Emergency Position Indicating Beacon (EPIRB)
ER - Engine Room Monitoring Systems
GP - Global Positioning System (GPS)
HC - Heading – Magnetic Compass
HE - Heading – North Seeking Gyro
HN - Heading – Non North Seeking Gyro
II - Integrated Instrumentation
IN - Integrated Navigation
LC - Loran C
P - Proprietary Code
RA - RADAR and/or ARPA
SD - Sounder, Depth
SN - Electronic Positioning System, other/general
SS - Sounder, Scanning
TI - Turn Rate Indicator
VD - Velocity Sensor, Doppler, other/general
DM - Velocity Sensor, Speed Log, Water, Magnetic
VW - Velocity Sensor, Speed Log, Water, Mechanical
WI - Weather Instruments
YX - Transducer
ZA - Timekeeper – Atomic Clock
ZC - Timekeeper – Chronometer
ZQ - Timekeeper – Quartz
ZV - Timekeeper – Radio Update, WWV or WWVH
Supported sentences
AAM - Waypoint arrival alarm
AAM_ARIV_ENT - Arrival circle entered
AAM_PERP_PASS - Perpendicular passed
AAM_CIRCLE_RAD - Circle radius
AAM_CIRCLE_RAD_UNIT - Circle radius units
AAM_WPTNAME - Waypoint name
ALM - GPS Almanac data
ALM_SENT_NUM - Number of sentences
ALM_SENT_CNT - Sentence count
ALM_PRN_ID - Satellite PRN number
ALM_WEEK_NO - GPS week number
ALM_SV_HEALTH - SV health
ALM_ECCENTRICITY - Eccentricity
ALM_REF_TIME - Almanac reference time
ALM_INC_ANGLE - Inclination angle
ALM_RA_RATE - Rate of right ascension
ALM_AXIS_ROOT - Root of semi-major axis
ALM_PEREGREE_ARG - Argument of perigee
ALM_NODE_LONG - Longitude of ascension node
ALM_MEAN_ANN - Mean anomaly
ALM_F0_CLOCK - F0 clock parameter
ALM_F1_CLOCK - F1 clock parameter
APA - Auto pilot A sentence
APA_STATUS1 - Loran-C blink/SNR warning, general warning
APA_STATUS2 - Loran-C cycle warning
APA_CROSS_TRACK_RAD - Cross-track error distance
APA_STEER - Steer to correct
APA_CROSS_TRACK_RAD_UNIT - Cross-track error units
APA_ARIV_ALRM_C - Arrival alarm - circle
APA_ARIV_ALRM_P - Arrival alarm - perpendicular
APA_MAG_BEAR_OD - Magnetic bearing, origin to destination
APA_MAG_BEAR_OD_UNIT - Magnetic bearing unit
APA_DEST_WPTID - Destination waypoint ID
APB - Auto pilot B sentence
APB_STATUS1 - Loran-C blink/SNR warning, general warning
APB_STATUS2 - Loran-C cycle warning
APB_CROSS_TRACK_RAD - Cross-track error distance
APB_STEER - Steer to correct
APB_CROSS_TRACK_RAD_UNIT - Cross-track error units
APB_ARIV_ALRM_C - Arrival alarm - circle
APB_ARIV_ALRM_P - Arrival alarm - perpendicular
APB_MAG_BEAR_OD - Magnetic bearing, origin to destination
APB_MAG_BEAR_OD_UNIT - Magnetic bearing unit
APB_DEST_WPTID - Destination waypoint ID
APB_MAG_BEAR_PD - Magnetic bearing, present position to destination
APB_MAG_BEAR_PD_UNIT - Magnetic bearing unit
APB_MAG_BEAR_HS - Magnetic heading to steer
APB_MAG_BEAR_HS_UNIT - Magnetic heading unit
BEC - Bearing and distance to waypoint – dead reckoning
BEC_UTC - UTC time of fix
BEC_WPT_LAT - Latitude of waypoint
BEC_WPT_LAT_H - Latitude hemisphere
BEC_WPT_LONG - Longitude of waypoint
BEC_WPT_LONG_H - Longitude hemisphere
BEC_BEARING - Bearing to waypoint
BEC_BEAR_TYPE - Bearing to waypoint type
BEC_DIST - Distance to waypoint
BEC_DIST_UNIT - Distance to waypoint units
BEC_WPTID - Waypoint ID
BOD - Bearing origin to destination
BOD_BEARING - Bearing from START to DEST, degrees
BOD_BEAR_TYPE - Bearing from START to DEST type
BOD_DEST_WPTID - Destination waypoint ID
BOD_ORIG_WPTID - Origin waypoint ID
BWC - Bearing using great circle route
BWC_DEPTH - Depth
BWC_DEPTH_UNIT - Depth unit
DBS - Depth below surface
DBS_DEPTH - Depth, meters
DBS_OFFSET - Offset from transducer
FSI - Frequency set information
FSI_TX_FREQ - Transmitting frequency
FSI_RX_FREQ - Receiving frequency
FSI_COMM_MODE - Communications mode
FSI_POWER_LEVEL - Power Level
GGA - GPS fix data
GGA_TAKEN_AT - Fix taken at
GGA_LATITUDE_DEG - Latitude
GGA_LATITUDE_DEG_H - Latitude hemisphere
GGA_LONGITUDE_DEG - Longitude
GGA_LONGITUDE_DEG_H - Longitude hemisphere
GGA_QUALITY - Fix quality
GGA_SAT_NUM - Number of satellites being tracked
GGA_HOR_DIL - Horizontal dilution of position
GGA_ALTITUDE - Altitude above mean sea level
GGA_ALTITUDE_UNIT - Altitude units
GGA_HEIGHT_OF_GEOID - Height of geoid (mean sea level) above WGS84 ellipsoid
GGA_HEIGHT_OF_GEOID_UNIT - Height of geoid units
GGA_TIME_SNC_DGPS - Time in seconds since last DGPS update
GGA_DGPS_ID - DGPS station ID number
GLC - Geographic position, Loran-C
GLC_GRI_MS - GRI Microseconds
GLC_TOA_MS - Master TOA microseconds
GLC_TOA_STATUS - Master TOA signal status
GLC_TIME_DIFF_MS - Time difference in microseconds
GLC_TIME_DIFF_STATUS - Time difference signal status
GLL - Geographic position, lat/lon data
GLL_LATITUDE_DEG - Latitude
GLL_LATITUDE_DEG_H - Latitude hemisphere
GLL_LONGITUDE_DEG - Longitude
GLL_LONGITUDE_DEG_H - Longitude hemisphere
GLL_TAKEN_AT - Fix taken at
GLL_STATUS - Status
GSA - Overall satellite data
GSA_AUTO_SEL - Auto selection of 2D or 3D fix
GSA_3D_FIX - 3D fix
GSA_SAT_PRN - Sat used for fix
GSA_PDOP - Dilution of precision
GSA_HDOP - Horizontal dilution of precision
GSA_VDOP - Vertical dilution of precision
GSV - Detailed satellite data
GSV_SENT_NUM - Number of sentences
GSV_SENT_CNT - Sentence count
GSV_SAT_IN_VIEW - Number of satellites in view
GSV_SAT_PRN - Satellite PRN number
GSV_ELEVATION - Elevation, degrees
GSV_AZIMUTH - Azimuth, degrees
GSV_SNR - SNR - higher is better
GTD - Geographic location in time differences
GTD_TIME_DIFF - Time difference
HDG - Heading, deviation and variation
HDG_MAG_HEAD - Magnetic sensor heading in degrees
HDG_MAG_DEV - Magnetic deviation in degrees
HDG_MAG_DEV_DIR - Magnetic deviation direction
HDG_MAG_VAR - Magnetic variation in degrees
HDG_MAG_VAR_DIR - Magnetic variation direction
HDM - Heading, magnetic
HDM_HEADING - Heading in degrees
HDM_HEADING_UNIT - Heading unit
HDT - Heading, true
HDT_HEADING - Heading in degrees
HDT_HEADING_UNIT - Heading unit
LCD - Loran-C signal data
LCD_GRI_MS - GRI Microseconds
LCD_MR_SNR - Master relative SNR
LCD_MR_ECD - Master relative ECD
LCD_TIME_DIFF_MS - Time difference in microseconds
LCD_TIME_DIFF_STATUS - Time difference signal status
MSK - Send control for a beacon receiver
MSK_FREQ - Frequency
MSK_FREQ_MODE - Frequency mode
MSK_BITRATE - Bitrate
MSK_BITRATE_MODE - Bitrate mode
MSK_FREQ_STATUS - Frequency for MSS message status
MSS - Beacon receiver status information
MSS_SIGNAL_S - Signal strength in dB
MSS_SIGNAL_N - Signal to noise ratio in dB
MSS_BEACON_FREQ - Beacon frequency in KHz
MSS_BEACON_BITRATE - Beacon bitrate in bps
MTW - Water temperature
MTW_DEGREES - Degrees
MTW_DEGREES_UNIT - Unit of measurement
MWV - Wind speed and angle
MWV_ANGLE - Wind angle
MWV_REF - Reference
MWV_SPEED - Wind speed
MWV_SPEED_UNIT - Wind speed unit
MWV_STATUS - Status
OSD - Own ship data
OSD_HEADING - Heading true, degrees
OSD_STATUS - Status
OSD_VESSEL - Vessel сourse true, degrees
OSD_VESSEL_REF - Course reference
OSD_VESSEL_SPEED - Vessel speed
OSD_SPEED_REF - Speed reference
OSD_VESSEL_SET - Vessel set true, degrees
OSD_VESSEL_DRIFT - Vessel drift true, degrees
OSD_VESSEL_DRIFT_UNIT - Vessel drift unit
ROO - Waypoints in active route
ROO_WPT_ID - Waypoint identifier
RMA - Recommended minimum navigation information
RMA_STATUS - Status
RMA_LATITUDE_DEG - Latitude
RMA_LATITUDE_DEG_H - Latitude hemisphere
RMA_LONGITUDE_DEG - Longitude
RMA_LONGITUDE_DEG_H - Longitude hemisphere
RMA_TIME_DIFF_A - Time difference A
RMA_TIME_DIFF_B - Time difference B
RMA_SPEED - Speed over the ground in knots
RMA_TRACK_ANGLE - Track angle in degrees
RMA_MAGN_VAR - Magnetic variation
RMA_MAGN_VAR_H - Magnetic variation hemisphere
RMB - Recommended minimum navigation information
RMB_STATUS - Status
RMB_CROSS_TRACK_ERR - Cross-track error
RMB_CROSS_TRACK_ERR_DIR - Cross-track error steer
RMB_ORIG_WPTID - Origin waypoint ID
RMB_DEST_WPTID - Destination waypoint ID
RMB_WPT_LAT - Latitude of destination waypoint
RMB_WPT_LAT_H - Latitude hemisphere
RMB_WPT_LONG - Longitude of destination waypoint
RMB_WPT_LONG_H - Longitude hemisphere
RMB_RANGE - Range to destination, nautical miles
RMB_BEAR - True bearing to destination
RMB_BEAR - Velocity towards destination, knots
RMB_ARIV_ALRM - Arrival alarm
RMC - Recommended minimum navigation information
RMC_TAKEN_AT - Fix taken at
RMC_STATUS - Status
RMC_LATITUDE_DEG - Latitude
RMC_LATITUDE_DEG_H - Latitude hemisphere
RMC_LONGITUDE_DEG - Longitude
RMC_LONGITUDE_DEG_H - Longitude hemisphere
RMC_SPEED - Speed over the ground in knots
RMC_TRACK_ANGLE - Track angle in degrees
RMC_DATE - Date
RMC_MAGN_VAR - Magnetic variation
RMC_MAGN_VAR_H - Magnetic variation hemisphere
ROT - Rate of turn
ROT_RATE_OF_TURN - Rate of turn, degrees per minute
ROT_STATUS - Status
RPM - Revolutions
RPM_SOURCE - Source
RPM_NUM - Engine or shaft number
RPM_SPEED - Speed, revolutions per minute
RPM_PITCH - Propeller pitch, % of maximum
RPM_STATUS - Status
RSA - Rudder sensor angle
RSA_SR_SENSOR - Starboard (or single) rudder sensor
RSA_STATUS - Starboard rudder sensor status
RSA_PR_SENSOR - Port rudder sensor
RSA_STATUS - Port rudder sensor status
RSD - Radar system data
RSD_CURSOR_RANGE - Cursor range from own ship
RSD_CURSOR_BEARING - Cursor bearing CW from zero, degrees
RSD_RANGE_SCALE - Range scale
RSD_RANGE_UNIT - Range units
RTE - Route message
RTE_SENT_NUM - Number of sentences
RTE_SENT_CNT - Sentence count
RTE_TYPE - Type
RTE_TYPE_NAME - Type name
RTE_ID - Route identifier
RTE_WPT_ID - Waypoint identifier
SFI - Scanning frequency information
SFI_SENT_NUM - Number of sentences
SFI_SENT_CNT - Sentence count
SFI_FREQ - Frequency
SFI_MODE - Mode
STN - Multiple data ID
STN_ID - Talker ID number
TTM - Tracked target message
TTM_TARGET_NUM - Target number
TTM_TARGET_DIST - Target distance
TTM_BEARING - Bearing from own ship
TTM_BEAR_TYPE - Bearing units
TTM_TARGET_SPEED - Target speed
TTM_TARGET_COURSE - Target course
TTM_COURSE_UNIT - Course units
TTM_DIST_CPA - Distance of closest-point-of-approach
TTM_TIME_CPA - Time until closest-point-of-approach '-' means increasing
TTM_SIGN - '-' means increasing
TTM_TARGET_NAME - Target name
TTM_TARGET_STATUS - Target status
TTM_REF_TARGET - Reference target
VBW - Dual ground/water speed
VBW_WATER_LONG_SPEED - Longitudinal water speed
VBW_WATER_TRAV_SPEED - Transverse water speed
VBW_WATER_STATUS - Water speed status
VBW_GROUND_LONG_SPEED - Longitudinal ground speed
VBW_GROUND_TRAV_SPEED - Transverse ground speed
VBW_GROUND_STATUS - Ground speed status
VDR - Set and drift
VDR_DEGRESS - Degress
VDR_DEGRESS_TYPE - Degress type
VDR_SPEED - Speed
VDR_SPEED_UNIT - Speed units
VHW - Water speed and heading
VHW_DEGRESS - Degress
VHW_DEGRESS_TYPE - Degress type
VHW_SPEED - Speed
VHW_SPEED_UNIT - Speed units
VLW - Distance traveled through water
VLW_TOTAL - Total cumulative distance
VLW_TOTAL_UNIT - Total cumulative distance unit
VLW_RESET - Distance since Reset
VLW_RESET_UNIT - Distance since Reset unit
VPW - Speed, measured parallel to wind
VPW_SPEED - Speed
VPW_SPEED_UNIT - Speed units
VTG - Vector track an speed over the ground
VTG_MAG_TRACK - Track made
VTG_MAG_TRACK_TYPE - Track made type
VTG_SPEED - Ground speed
VTG_SPEED_UNIT - Ground speed units
VWR - Relative wind speed and angle
VWR_WIND_DIR - Wind direction magnitude in degrees
VWR_WIND_DIR_TYPE - Wind direction type
VWR_SPEED - Speed
VWR_SPEED_UNIT - Speed units
WCV - Waypoint closure velocity
WCV_VELOCITY - Velocity
WCV_VELOCITY_UNIT - Velocity units
WCV_WPT_ID - Waypoint identifier
WNC - Distance, waypoint to waypoint
WNC_DISTANCE - Distance
WNC_DISTANCE_UNIT - Distance units
WNC_DEST_WPTID - Destination waypoint ID
WNC_ORIG_WPTID - Origin waypoint ID
WPL - Waypoint information
WPL_LATITUDE_DEG - Latitude
WPL_LATITUDE_DEG_H - Latitude hemisphere
WPL_LONGITUDE_DEG - Longitude
WPL_LONGITUDE_DEG_H - Longitude hemisphere
WPL_WPTNAME - Waypoint name
XDR - Multiple cross track error, dead reckoning
XDR_TRANS_TYPE - Transducer type
XDR_MEASURE_DATA - Measurement data
XDR_MEASURE_UNIT - Measurement data units
XDR_TRANS_NAME - Name of transducer
XTE - Measured cross track error
XTE_GEN_WARN - General warning flag
XTE_LORAN_LOCK - Loran-C cycle lock flag
XTE_CROSS_TRACK_DIST - Cross track error distance
XTE_STEER - Steer
XTE_DIST_UNIT - Distance units
XTR - Cross track error, dead reckoning
XTR_TRANS_TYPE - Transducer type
XTR_MEASURE_DATA - Measurement data
XTR_MEASURE_UNIT - Measurement data units
XTR_TRANS_NAME - Name of transducer
ZDA - Date and Time
ZDA_TIME - Time
ZDA_DAY - Day
ZDA_MONTH - Month
ZDA_YEAR - Year
ZDA_ZONE_HOUR - Local zone hours
ZDA_ZONE_MIN - Local zone minutes
ZFO - UTC and time to destination waypoint
ZFO_TIME - Time
ZFO_TIME_REMAIN - Time remaining
ZFO_WPT_ID - Waypoint identifier
GRMC - Sensor configuration information
GRMC_MODE - Fix mode
GRMC_ALT - Altitude above/below mean sea level
GRMC_DATUM_INDEX - Earth datum index
GRMC_DATUM_AXIS - User earth datum semi-major axis
GRMC_DATUM_FACTOR - User earth datum inverse flattening factor
GRMC_DATUM_DELTA_X - User earth datum delta x earth centered coordinate
GRMC_DATUM_DELTA_Y - User earth datum delta y earth centered coordinate
GRMC_DATUM_DELTA_Z - User earth datum delta z earth centered coordinate
GRMC_DIFF_MODE - Differential mode
GRMC_BAUD_RATE - NMEA Baud rate
GRMC_FILTER_MODE - Filter mode
GRMC_PPS_MODE - PPS mode
GRME - Estimated position error
GRME_HPE - Estimated horizontal position error (HPE)
GRME_HPE_UNIT - HPE units
GRME_VPE - Estimated vertical error (VPE)
GRME_VPE_UNIT - VPE units
GRME_OSEPE - Overall spherical equivalent position error (OSEPE)
GRME_OSEPE_UNIT - SEPE units
GRMF - Position fix sentence
GRMF_WEEK_NO - GPS week number
GRMF_SEC_NUM - GPS seconds
GRMF_UTC_DATE - UTC date of position fix
GRMF_UTC_TIME - UTC time of position fix
GRMF_LEAP_SEC_NUM - GPS leap second count
GRMF_LATITUDE_DEG - Latitude
GRMF_LATITUDE_DEG_H - Latitude hemisphere
GRMF_LONGITUDE_DEG - Longitude
GRMF_LONGITUDE_DEG_H - Longitude hemisphere
GRMF_MODE - Mode
GRMF_FIX_TYPE - Fix type
GRMF_SPEED - Speed over ground, km/h
GRMF_COURSE - Course over ground, degrees
GRMF_DIL_POS - Position dilution of precision
GRMF_TIME_DIL_POS - Time dilution of precision
GRMI - Sensor initialization information
GRMI_LATITUDE_DEG - Latitude
GRMI_LATITUDE_DEG_H - Latitude hemisphere
GRMI_LONGITUDE_DEG - Longitude
GRMI_LONGITUDE_DEG_H - Longitude hemisphere
GRMI_UTC_DATE - Current UTC date
GRMI_UTC_TIME - Current UTC time
GRMM - Map datum
GRMM_DATUM - Currently active horizontal datum
GRMO - Output sentence enable/disable
GRMO_NAME - Target sentence description
GRMO_MODE - Target sentence mode
GRMV - 3D velocity
GRMV_EAST_VEL - True east velocity
GRMV_NORTH_VEL - True north velocity
GRMV_UP_VEL - Up velocity
GRMZ - Altitude information
GRMZ_ALT - Altitude
GRMZ_ALT_UNIT - Altitude units
GRMZ_POS_FIX_DIM - Position fix dimensions
SLIB - Differential GPS beacon receiver control
SLIB_FREQ - Frequency
SLIB_BITRATE - Bit rate
SLIB_REQ_TYPE - Request type
SRF150 - OK to send
SRF150_STATUS - Status
SRF161 - OK to send
SRF161_ANT_STATUS - Antenna status
SRF161_AGC - AGC
Window view
This tab in program options (fig. 26) allows you to customize the appearance of the main window of the program (fig.1). You can access this tab through the "Options → Program options" menu item in the main window.
Fig. 26. Window view setting
You can set the following parameters:
•Start in minimized state - at start Advanced NMEA Data Logger will automatically minimize the program window to the taskbar or to the Systray (fig. 27).
•Minimize to Systray - while the main window of Advanced NMEA Data Logger minimizes, the program will automatically put its icon to the system panel near the clock.
•Show data window - if you specify this option, then the program will display all data in the main window. You may disable this option if you log data from many ports on a slow computer. It reduces the computer's CPU usage.
•Output data on screen in minimized state - if you'll enable this option, then the program will display processed data in minimized state. If you are logging many data sources on a slow computer, then you can decrease computer central processor load rate with disabling of this option.
•Font type - the data will be displayed with this font type in the main window. We recommend using mono-spaced fonts in this field, such as Terminal, Courier, or System.
•Screen buffer - when the number of lines in the main window exceeds the specified value, the program deletes old lines from the screen buffer.
•Window view - this option group lets you configure data window view mode (a font color, a font type, a background color).
•Transparency - in modern OS, it lets you set the transparency of the main window. The most left position is the normal window view, and the most right position is maximum transparency.
•Wrap words - if you didn't configure a parser module or your data flow doesn't contain a blocks separator, then your data without this option enabled will be displayed as one long string in the data window.
Fig. 27. Systray - panel near clock
Date/time stamp view
This group of options (fig. 28) allows configuring the format of date/time stamps that will be used in the main program window and log files.
Fig. 28. Configuring data/stamp view
Prefix/Postfix characters for display output - these options allow you to define the beginning and ending characters of a date/time stamp that will be shown in the program window. When outputting data to a log file, the program uses individual characters for each configuration.
View mode - allows you to select the standard or define the custom format of the date/time stamp.
Font - this group allows you to define the color and font of date/time stamp.
Add data direction sign to a stamp - if this option is activated, then the program will append TX or RX to the end of the stamp.
Add data source ID to a stamp - if this option is activated then the program will data append data source ID at the beginning of the stamp, for example, COM1.
Protocol and errors handling
While the program is running, it may generate many messages about errors or events. All these messages are being registered in a protocol file. The protocol file may contain messages from the main program and all working plugins. On this tab, you can define the kind of messages, which you want to put a protocol file (fig. 29). Here you can set the maximum protocol file size and the formatting mode.
Usually, the protocol file is in the "AppData" folder and has the name of the program with the 'log' extension.
On Windows 7 and higher: c:\ProgramData\Advanced NMEA Data Logger\
On old OS: c:\Document and Settings\All Users\Advanced NMEA Data Logger\
You can also open the protocol file from the “File” menu in the main window.
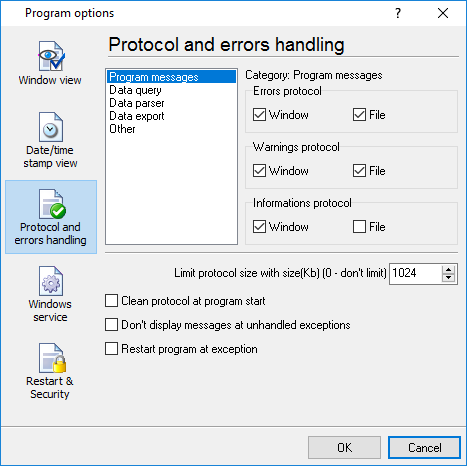
Fig. 29. Protocol settings
Advanced NMEA Data Logger works with three types of messages:
•Information messages - this type of messages informs you about current operations.
•Warnings - warns you about possible failures or errors. Immediately user reaction is not required.
•Errors - the program has detected an error which requires user attention.
There is the possibility to log the following events:
•Program messages - messages about start or stop of the program, etc.
•Data query - messages which are generated in a data query module.
•Data parser - messages from a data parser module.
•Data export - messages issued by a data export module.
•Other - other message types.
You can write each type of messages to a protocol file or/and to the list in the main window. Please, specify necessary options for each message type at "Window" and "File" fields.
If you don't want to allow growing a protocol file size to an unlimited size, then you can enable the "Clean protocol at program start" or limit protocol file size in the "Size" field.
Some exceptional (unhandled) messages may occur while the program is running. In most cases, these messages affect the program, and the safest way is to restart the program. Please, specify the "Restart program at exception" option and the program will be restarted automatically.
If you want to look all program messages, then you can disable the "Don't display messages at unhandled exceptions" checkbox, and the program will open the exception message window with detailed information.
Configuration
Windows 2000+ services let you:
•Control service on local and remote computers, including remote computers with Windows 2000+ system.
•Setup actions on emergency service restore in case of failure, for example, auto service or computer restart (only on computers with Windows 2000 or later).
•Create for services other names and descriptions, to find them easier (only on computers with system Windows 2000 or later).
•Run service before user login (password input).
•Service can be configured on automatic start after operation system load.
Note 1: you must be logged in as an administrator to change the configuration or control the service in any way (start, stop, pause, continue).
Note 2: On Windows Vista and later you should start the program with elevated administrator privileges.
If you want to use the program as a service application, then, please, go to the "Options → Program options → Windows service" tab (fig. 30), then enable the "Use program as a service" checkbox. Later, please, specify the start-up type of the service. There are the following variants:
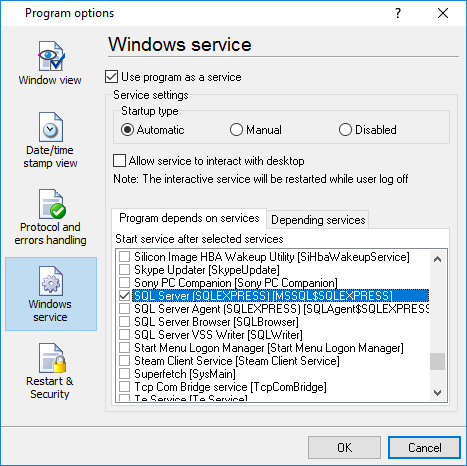
Fig. 30. Service settings
1.Automatic - the service starts automatically with Windows, before user login.
2.Manual - you can start the service application from the "Services" control panel (fig. 33).
3.Disabled - the service is disabled, and does not start at all.
If you want to change the program settings while the program works in the service mode, you can start a second instance of the program on your desktop, make the necessary changes, and restart the service with the new settings.
Old Windows versions (before Windows Vista) allows you to use the service in the interactive mode. In this case, the program places an icon in the system area (fig. 31).

Fig. 31. Service icon in Systray
If the service should write data a database or use another service on your computer, they should be started before Advanced NMEA Data Logger. You can configure a list of these services on the "Program depends on services" tab (fig. 32).
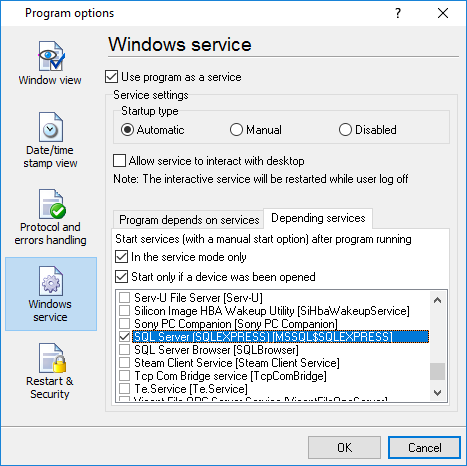
Fig. 32. Service settings #2
Sometimes, you may need to start Advanced NMEA Data Logger before starting other services. In this case, you should:
•Switch the start mode of a target service to "Manual."
•Start Advanced NMEA Data Logger.
•Select the necessary service on the "Depending services" tab.
•Select the mode when the logger will start the selected service.
•Restart Advanced NMEA Data Logger.
After you configured Advanced NMEA Data Logger to work in the service mode, you need to restart a computer or start the service manually from the "Services" control panel (fig. 33).
Fig. 33. Manual service run (in Windows 2000)
When the service is running, two processes should appear in the Task Manager: nmealoggersrv.exe and nmealogger.exe (fig. 34). The 'nmealoggersrv.exe' application implements an interface between the service manager and the Advanced NMEA Data Logger software. Unlike srvany.exe utility, our service stops safely.
Fig. 34. Process list
If you want to configure the program as a service, then you must be logged with administrator rights. The service application can be controlled, stopped, or removed with the help of a command-line. Run nmealoggersrv.exe with the following parameters:
•/? - a short help.
•/I - install service for starting in then manual mode.
•/A - install service for starting in the automatic mode.
•/D - install service in the disabled state.
•/R - remove service from the computer.
Windows Vista+ notes
One of the ways Vista's security was improved was by separating system services and user applications into separate 'sessions'. Keeping the system services isolated helps to secure them better, but also makes any interactive interface unavailable to the user. That's where the Interactive Services Detection service comes in. When a service needs to interact with the user, Interactive Services Detection presents a dialog that will switch the user to the session where the service is running so they can interact with the service. For an excellent, detailed description of this, see next paragraph.
Many sites recommend disabling this service, but doing so will result in you not being able to interact with any services that require your attention. This service is run manually by default, so there is little point to disabling it unless you don't want to be bothered by important information from the software you may be trying to run.
•Display Name: Interactive Services Detection
•Service Name: UI0Detect
•Process Name: UI0Detect.exe
•Description: Enables user notification of user input for interactive services, which enables access to dialogs created by interactive services when they appear. If this service is stopped, notifications of new interactive service dialogs will no longer function, and there may no longer be access to interactive service dialogs. If this service is disabled, both notifications of and access to new interactive service dialogs will no longer function.
•Path to Executable: %windir%\system32\UI0Detect.exe
•Default Start-up:
1.Home Basic: Manual
2.Home Premium: Manual
3.Business: Manual
4.Enterprise: Manual
5.Ultimate: Manual
Restart & Security
Sometimes the program should be restarted. For example, if you've changed the program settings remotely and want to reload program automatically with the new settings. To do that, specify the time for restarting the program on the "Restart & Security" tab in program options "Options - Program options". Just specify the time of day, when the program should be being restarted.
Fig. 35. Program restart settings
On this tab, you can also protect some actions with the program by a password. To do that, activate the "Protect by password" option, define a password and select protectable actions.
Program doesn't run or work
It is necessary to make sure in proper time installation on your computer, so as if you put clock after program installation, protection from use after trial period works.
Also, the program will not work, if you use a software debugger in your environment like WinDbg. In any other case, please, contact us on support page.
FAQ
Question: Does the program work with virtual COM ports? USB-COM converters?
Answer: Absolutely!
Question: Why COM port doesn't open?
Answer: Probably, another program already uses it (the selected COM port). It can be a service application, for example.
Question: What to do?
Answer: Close the application that uses this communicative port (for a DOS application close also a DOS session window). Alternatively, use another communicative port. Probably, a COM port wasn't properly closed.
Question: Is it possible to set variable data transmit rate or transmit 9 data bits?
Answer: No, the Windows operating system doesn't have such the feature.
Question: What socket type to use: DB25 or DB9?
Answer: It does not matter. All modern computers have DB9 only. Alternatively, they do not have DB9 sockets at all.
Question: What cable do I need: straight or crossed (null-modem)?
Answer: It depends on your device. Generally, you should use a null-modem (crossed) cable with the following layout:
Device | Computer
_____________
RXD <-→ TXD
TXD <-→ RXD
GND <-→ GND
If a device uses special signals like DTR or RTS, and you don't want to use hardware data transmit control, you need to connect pins 7 and 8 of the DB9 socket on the device side.
You can find more hardware related articles on our site https://www.aggsoft.com.