Write Data to RFID Tags: Change EPC Identifier with LLRP Software
Write data to the tag's memory or change of the tag's EPC identifier
You can use the "Write" tab (Figure 16) to write data to the tag's memory (if the tag supports that action). This feature can be used only with tags that support the "Class-1 Gen-2" standard.
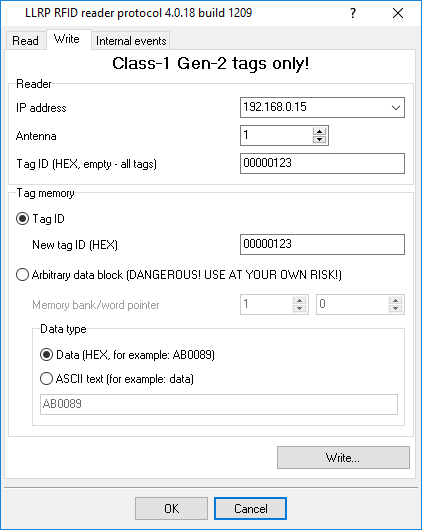
Figure 16: Writing data to the tag's memory
IP address - The reader's IP address. The reader should be duly configured, its IP address should be specified in the TCP/IP settings (see "Configuring the connection with the reader"), and a connection with the reader should be established.
Antenna - The reader's antenna number that can perform the write operation to the tag.
Tag ID - A unique identifier of the tag in HEX format.
Select the data writing mode in the "Tag memory" parameter group.
New tag ID - A new tag identifier. The application will automatically write the new identifier to the correct memory area.
Arbitrary data block - You can write any data block to any memory bank, starting from any memory cell.
Memory bank - The number of the memory bank:
- 0 - Reserved block.
- 1 - Memory block for storing the identifier.
- 2 - Memory block of the TID type.
- 3 - Memory block for storing user data.
WORD pointer — The start memory cell address for writing data. Memory cell numbering starts from 0. Each cell's size is 2 bytes (WORD data type).
Note 1: A memory cell address should be specified, not a byte address in the memory. As each cell contains 2 bytes, the size of data written (in bytes) should be a multiple of two.
Note 2: The size of each memory block depends on the tag's maker.
Related articles: Write Data to RFID Tags: Change EPC Identifier with LLRP Software
RFID
Related topics: Advanced Serial Data Logger
hereSerial port interface | RS232 port logger | Com port logger | Data acquisition | RS232 data logger | Data Logger Software For Electricity Meter | RS232 to ODBC | RS232 to MySQL | RS232 to MS SQL Server | RS232 to database | Barcode to Excel